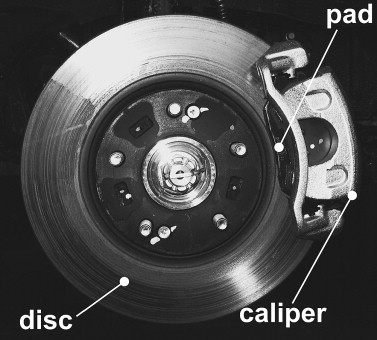
 Disc brake drag is when your brakes fail to release completely after you have removed your foot from the brake pedal. As you may already know, the continuous use of your brakes may cause them to overheat—brake drag is problematic because the brakes would remain applied which results in overheating and damaged parts. Let us begin by mentioning that a little brake drag is normal and brake pads and rotors are usually in slight contact. If you were to spin your wheel, the wheel should be able to partly turn on its own. If the wheel does not spin and there is a lot of turning resistance, then there may be more brake drag present than you want. One main cause of disc brake drag involves the brake calipers.
Disc brake drag is when your brakes fail to release completely after you have removed your foot from the brake pedal. As you may already know, the continuous use of your brakes may cause them to overheat—brake drag is problematic because the brakes would remain applied which results in overheating and damaged parts. Let us begin by mentioning that a little brake drag is normal and brake pads and rotors are usually in slight contact. If you were to spin your wheel, the wheel should be able to partly turn on its own. If the wheel does not spin and there is a lot of turning resistance, then there may be more brake drag present than you want. One main cause of disc brake drag involves the brake calipers.
*Photo Source: www.sciencedirect.com
Brake calipers are responsible for bringing the brake pads and brake rotors into contact to stop your vehicle. There are sliding mechanisms in a brake caliper that allow it to close onto the brake rotor. Brake drag can be a result of the sliding components in a brake caliper being corroded or dirty, which prevents movement and causes seized calipers. Seized calipers may prevent the brakes from moving back to its resting position, which leads to the brakes dragging. The wisest thing to do in this situation would be to purchase a new caliper. A cheaper alternative would be to buy one rebuilt—do not attempt to refurbish or rebuild your own calipers as this may be very dangerous--only qualified personnel or experts should perform this sort of work.








crescent foundry
posted on Nov 29, 2022 1:27:58 AM